
CoQ10 facilitates the transformation of fats and sugars into energy inside the mitochondria.
Having the Best Life Boils Down to Having Enough Energy to Do The Things You Want To Do!
Don’t Let Low CoQ10 Drain Your Drive!
CoQ10 is essential for making ATP — the energy your cells run on. CoQ10 levels decline with age, stress, and statin use. When CoQ10 drops, so can your ability to stay energized, focused, and resilient.
Smart people prioritize CoQ10 — because low levels can quietly limit how alive you feel.
If we compared our cellular mitochondria to a car engine, CoQ10 would be the fuel injector (or carburetor and spark blugs for older cars) that increases the efficiency of fuel burning.
Since nothing is more basic to life than burning of fuel to make energy it follows that when CoQ10 levels diminish, basic cell metabolic functions are impaired, and the ability to live a productive life must necessarily diminish.
It is interesting that by the time someone reaches 80 years of age, 80% of the CoQ10 molecules that were in a person’s cells at age 25 are gone. By age 80, the pancreas which is responsible for digestive enzymes has lost 83% of its youthful CoQ10 levels. With less enzymes, no wonder we cannot digest our foods well as we used to. So, for people with poor digestion, CoQ10 supplementation is a must!
If you're over the age of 30, one of your first tactics for improving energy and preserving future health and longevity is supplementing with CoQ10.
CoQ10 Decreases in Human Tissues as We Age
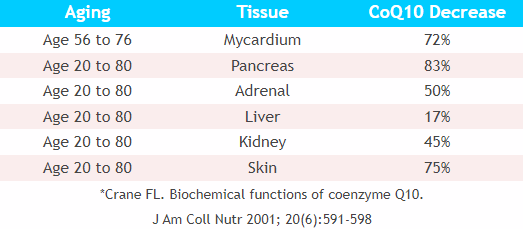
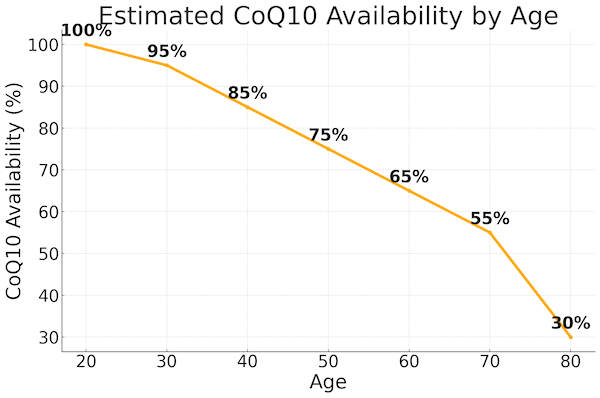
Looking at the above charts/graphs... No wonder we notice a difference in how we feel as we age.
- No wonder CoQ10 has drawn interest from supplement formulators around the globe—cellular energy production isn’t exactly what it used to be.
- No wonder so many people notice changes in how their body performs when they support their mitochondria.*
- No wonder skin, of all things, has a way of showing us how time affects inner biology.*
- No wonder the pancreas—an unsung hero—seems to quietly demand more attention over time.*
- No wonder those pivotal years between 56 and 76 often tell a tale about what we’ve supported… and what we haven’t.*
*These observations are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. They are simply patterns worth paying attention to.
Does It Matter Which Kind of CoQ10 We Take?
Some manufacturers promote reduced CoQ10 (ubiquinol) as significantly superior to the standard oxidized form (ubiquinone), but this claim appears more tied to marketing momentum than consistent science. Both forms are absorbed and interconverted by the body based on cellular demand. What appears to matter more is how CoQ10 is taken: when consumed with healthy fats and absorption-enhancing compounds like BioPerine (black pepper extract), bioavailability can increase substantially, regardless of the form.
However, What CoQ10 Is Taken With Does Matter
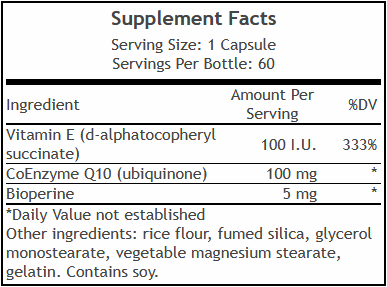
The absorption of CoQ10 may be influenced by what it’s consumed with. Nutrients such as **vitamin E**, **Bioperine® (black pepper extract)**, and **healthy dietary fats** have been shown to help enhance its uptake. Having one or more of these companions present in the stomach at the same time may support better delivery of CoQ10 into the bloodstream and ultimately into the cells. That’s one reason CoQ10 Plus E includes these cofactors in its formulation—because formulating for absorption can make all the difference.
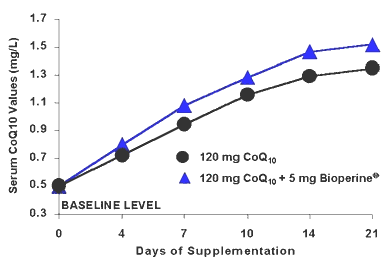
This graph shows the amount of CoQ10 going to the blood after a single oral intake of 90 mg CoQ10 and 5 mg of Bioperine.
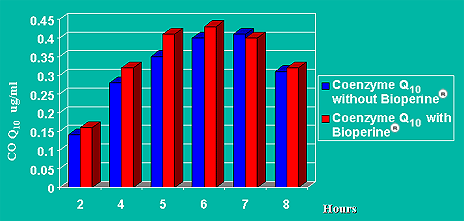
And the following graph shows the absolute change in serum CoQ10 after 14 days of supplementation with CoQ10 (90 mg daily) and Bioperine (5mg daily).
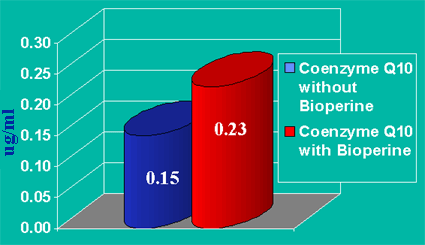
Finally, this graph shows the serum levels after a 21 day trial in terms of sustained CoQ10 increase.
Summary of CoQ10 Benefits:
- Supports mitochondrial function to help reduce oxidative stress and enhance cellular energy production—especially important for cardiovascular performance and heart health.*
- Emerging research suggests CoQ10 may support healthy aging by enhancing mitochondrial efficiency in the brain, lungs, and metabolic systems, including those related to blood sugar control.*
- Optimal mitochondrial health is essential for whole-body wellness, as mitochondria fuel nearly every cell in the body.*
- CoQ10 supplementation helps maintain coenzyme Q10 levels in a youthful range, which may support sustained vitality, endurance, and overall metabolic balance.*
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
What is an Optimal Daily Amount of CoQ10 Plus E To Take — By Age:
Note that we offer two CoQ10 products, one that is 100 mg per capsule (this one) and another that is 400 mg per capsule.
- 30s: 100 mg — 1 capsule AM
- 40s: 200 mg — 1 capsule AM and 1 at noon
- 50s: 300 mg — 1 capsule AM, 1 at noon, and 1 in PM
- 60s: 400 mg — 1 capsule AM, 2 at noon, and 1 in PM or just one of our larger dose capsule.
- 70s: 500 mg — 1 capsule AM, 2 at noon, and 2 in PM
- 80s: 600 mg — 2 capsules AM, 2 at noon, and 2 in PM or one capsule in morning and one in afternoon of our larger dose capsule.
- 90s: 800 mg — 1 400mg softgel AM, 1 400 mg softgel at noon
CoQ10 Plus E Ordering Form
Comparative Retail Price: $49.95 per bottle.
Our Price: $34.95 per 60 capsule count bottle
CoQ10 Plus E

How to Use
Take one to eight capsules daily, depending on age, quality of health and tolerance, and always take with food (to improve absorption).
Videos about CoQ10
We disclaim any claims (if there are any) made in these videos. They are for information, education, enlightenment and entertainment only.


