- Improving lives since 2002
- Fast, Friendly Service
- Free Nutritional Counseling
The key to health is eliminating toxicities and deficiencies! - Dr. William R. Kellas

Most people still think creatine is something for bodybuilders and gym devotees. But the truth? Creatine is one of the most researched, reliable, and effective supplements for nearly everyone — especially women, older adults, and anyone who wants more energy, strength, and mental sharpness.
Our ultra-pure, micronized creatine monohydrate mixes easily and is backed by decades of clinical research. Whether you’re walking the dog, chasing grandkids, rebuilding after illness, or just want your skin and body to look and feel younger — creatine powers your muscles, brain, and cellular energy systems to help you show up stronger, single day.

⚡ Think of creatine as your body’s cellular energy buffer — the molecule that helps recharge your energy system every time you think, move, breathe, or rebuild.
It works by rapidly recycling ATP, the fuel that powers nearly every process in your body.
Without enough creatine, your cells underperform — especially in your brain, muscles, and heart, where energy demands are highest.
Silky mixing. Transparent testing. Straight-up creatine monohydrate—no fluff, just results.
“Texture and taste (none) were great for mixing.”
“Mixed effortlessly with just a spoon in plain water, with zero chalkiness.”
*Dietary supplements aren’t intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent disease. Always consult your healthcare professional.
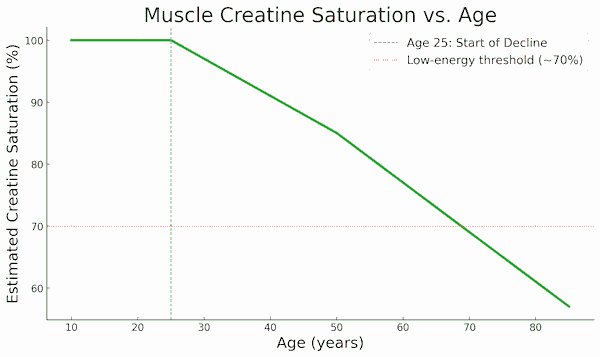
As we age, our body’s natural creatine production slows down — often falling by 30–40% by the time we reach our 60s. This decline contributes to fatigue, muscle loss, mental fog, and slower recovery. Here’s how to keep your creatine tank full:
Again, creatine isn’t just about performance — it’s about keeping the lights on in your most vital systems. Your energy, your clarity, your recovery — all depend on it. And it’s one of the easiest, safest, most affordable ways to support graceful, high-functioning aging.
Our creatine provides a simple, tasteless way to get the full researched dose — without needing to eat pounds of meat daily.
Comparative Retail Price: $29.95
Our Price: $27.95
Creatine Monohydrate


Creatine supports energy metabolism in muscles, the brain, and other high-demand tissues. It’s especially valuable for athletes, those with metabolic or liver challenges, individuals seeking fat loss, and even people looking to improve skin hydration and reduce facial wrinkles.*
For best results, take 1 to 2 teaspoons (3–5 grams) of creatine monohydrate once or twice daily. During intensive phases (e.g., bodybuilding, recovery, or visible aesthetic goals), some may take up to 3 servings per day under guidance.
Mix into warm water, juice, or any non-acidic liquid. Drink immediately. For enhanced absorption, take with a small amount of carbohydrate (like fruit or yogurt), unless following a ketogenic protocol.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
We disclaim any claims (if there are any) made in these videos or audios. They are for information, education, enlightenment and entertainment only.
Copyright 2002 - 2025. All rights reserved.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. No product mentioned herein is intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. If you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition, consult your physician before making any lifestyle change, including trying a new product or food.
The information on this website is intended as a sharing of knowledge and information from the research and experience of the Healthy-Living.Org staff and contributors. It is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and it is not intended as medical advice. You should not use the information on this site for diagnosis or treatment of any health problem or for modification of any medication regimen. You should consult with a healthcare professional before starting any diet, exercise or supplementation program, before starting or discontinuing any medication, or if you suspect you have a health problem. You should keep in mind that cited references to ongoing nutritional scientific study are most likely not accepted by the FDA as conclusive. These references and mentions of benefits experienced by others are disavowed as product claims and are only included for educational value and as starting points for your own research. No food or supplement can be considered safe for all individuals. What may benefit 999,999 of a million people may harm you. Therefore, no one can take responsibility for your health except you in concert with your trusted health professional.