- Improving lives since 2002
- Fast, Friendly Service
- Free Nutritional Counseling
The key to health is eliminating toxicities and deficiencies! - Dr. William R. Kellas
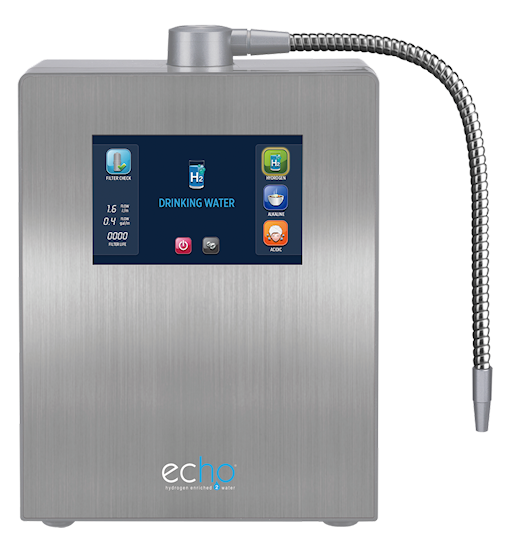

They are cutting-edge, third-generation PEM electrolysis machines that transform ordinary water into ultra-pure, hydrogen-rich water. These advanced systems not only remove chlorine and contaminants from the input water but also deliver 7 to 10 ppm of hydrogen-rich water directly into your glass—whether you need a single cup or thousands of gallons each month. Every ounce of water produced is infused with septillions of antioxidant hydrogen molecules, offering unmatched purity and health benefits
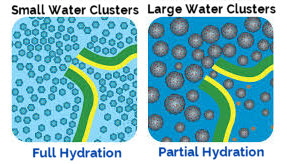
The Echo® Hydrogen-Rich Water Machines feature advanced Proton Exchange Membranes (PEM), surpassing traditional electrolysis technology. Unlike standard methods, PEM generates its own water conductivity, enabling hydrogen production even in pure water, such as reverse osmosis or distilled water. A standout feature of our machines is the creation of nano-sized hydrogen bubbles, ensuring higher hydrogen concentrations (ppm) and longer-lasting benefits. Additionally, our technology eliminates contact between the electrolysis electrodes and the output water, ensuring zero heavy metals in your hydrogen-rich drinking water — a significant advantage for purity and safety
Hydrogen is the smallest atom and molecule in the universe. Its small size allows it to get into membranes, joints, brain, gut, organs, lungs, eyes, ears, etc. Hydrogen can reach to every cell and corner of the body to extinguish free radicals. The reason it can do so is because its small size enables it to pass through cell membranes. In other words, as an antioxidant, hydrogen is unstoppable. No other type of antioxidant is more likely to extinguish the free radicals in your body.

When you rank the relative size of antioxidants, hydrogen atoms are 176 times smaller than vitamin c antioxidant molecules, 290 times smaller than green tea antioxidant molecules, 309 times smaller than glutathione antioxidant molecules, 431 times smaller than Vitamin E antioxidant molecules, and 863 times smaller than CoEnzyme Q10 antioxidant molcules. That's why Hydrogen is the best antioxidant. It's smaller and easily enters all the cells of the body to protect those cells from free radicals.
The daily routine of supplying one's cells with molecular hydrogen can help curtail the aging (oxidation) process, greatly reducing free radical damage and degradation of the cells and molecules of one’s body, hopefully, helping to delay or avoid pain, dysfunction, or disease processes in general. But, this benefit can only occur if one consumes an effective hydrogen product continuously.

We believe that having the hydrogen habit will help virtually anyone as follows:
Consistently drinking water that has been enriched with hydrogen is one of the most powerful health habits science that has discovered and can significantly delay deterioration of one’s physical and mental functioning. Thankfully, it's a habit that most people can afford... and the science is palpable, duplicable, absolutely real. So, that you will understand the power of hydrogen and not lose out on decades of healthy life, please click and watch the videos.
Our top-end Hydrogen Rich Water Machines saturate the output water with 7 to 9 ppm of hydrogen, which amounts to septillions of hydrogen molecules in just a few ounces of water. Those hydrogen elements are antioxidants that will reduce free radicals they encounter.

We disclaim any claims (if there are any) made in these videos. They are for information, education, enlightenment and entertainment only.

The redox reaction, or reduction-oxidation process, is the most universal, fundamental, as well as, most important of all processes in life. The problem of life and death as well as health and sickness could, therefore, be explained and demonstrated by the concept of redox reaction.
For every disease there is a single key mechanism that dominates all others. If one can find it and then think one's way around it, one can control the disorder. (Lewis Thomas, MD Sloan Kettering Hospital, NYC)
A single key mechanism that dominates all others is nothing but redox reaction. So that, if we can find a way to control it, we can conquer the disorder. Water rich in atomic as well as molecular hydrogen should be an ultimate solution for it as far as my theory is concerned. (H. Hayashi, MD Water Institute, Japan) Redox Reaction
We can recap these concepts with a following analogy. Copper (Cu) loses its glitter by oxidation and is restored by reduction. In quite the same way, a cell unit is damaged (made sick) by oxidation and is restored (cured) by reduction resulting in the production of H2O. And, since oxidation is the process by which energy is created... it is by nature, damaging to our mitochondria and cells and must be balanced by reduction.
Water or H2O is the very product of redox reaction, i.e., a product of reduction by Hydrogen and oxidation by Oxygen. Therefore, it is only natural to say that every life form, born in H2O should be under the influence of redox reaction. In short, oxidation brings it sickness and reduction restores it to health again. It is quite clear from the evolutionary record that water is the foundation of life, because it was an environment which provided them with all the necessary conditions for birth and survival.
Active oxygen species are considered to inactivate enzymes in the cells, damage DNA and destroy lipid membrane which should cause every disease, aging as well as cancer as far as the most recent medical research is concerned. In other words, if we can succeed in preventing oxidative damage by active oxygen species, we can control the disorder as far as my theory is concerned.
Then what is the most ideal countermeasure against active oxygen? It should be nothing but 'active hydrogen' as far as the logic is concerned. Active hydrogen or atomic hydrogen is known to have strong reducing potential. It is only natural to say that active oxygen species can be reduced or scavenged to produce O2-, H2O2 and HOE one after another to produce H2O as a result, as shown in the following.
(HE & HOE refer to hydrogenase enzyme chemical activity)
According to my concept, water can be classified into two kinds, i.e., hydrogen poor and hydrogen rich water.
Natural water or 99.9% of water found on the earth can be defined to be hydrogen poor water because of hydrogen bond energy connecting hydrogen with oxygen to make H2O. It is a logic of mine that natural water, hydrogen poor water, can't be enough to reduce or scavenge active oxygen species, which should have compelled us mankind to develop a procedure with which we can fight against sickness being brought as the result of oxidative damage by active oxygen.
In other words, human medicine, without reduction is a kind of fiction based system... following from intake of natural water or hydrogen poor water. On the contrary, we could easily be free from sickness if we depend on hydrogen rich water which can be enough to scavenge active oxygen species.
It is known that magnesium reacts with water to produce hydrogen gas when it is heated. We confirmed, however, that magnesium produces hydrogen gas even in water with room temperature which could be demonstrated by the Portable Hydrogen Detector developed by ourselves being explained in the following chemical formula.
Active hydrogen in Hydrogen Rich Water binds with active oxygen to produce H2O. Molecular hydrogen in Hydrogen Rich Water can be split to atomic hydrogen by hydrogenase in our body being implied by R. Happe in his paper 'EEE hydrogenases are enzymes that can reversibly split molecular hydrogen. EEE Ni/Fe hydrogenases are among the oldest enzymes ( 3.8 billion years old ), demonstrating early that life forms had developed an effective way to activate molecular hydrogen at ambient temperature and pH. (BIOLOGICAL ACTIVATION OF HYDROGEN ; NATURE,385,126,1997).
'Hydrogen Rich Water' can easily be obtained by utilizing the reaction of water with magnesium, hydrogen producing mineral, whose preparation is named the Hydrogen Producing Mineral Stick and is being presented by us for general use. Magnesium oxide has long been used in medicine as a antacid and laxative. Quite a new aspect of the mineral, producing ability of hydrogen to scavenge active oxygen has been clarified now for the first time by us.
Hidemitsu Hayashi, MD
August 11, 2001
According to Dr. Susanetta Shirahata (Graduate School of Genetic Resources Technology, Kyushu University), the so called miracle healing waters all contains molecular Hydrogen and the healing effect is simply the result of the health benefits of that Hydrogen.
Water Institute, and Munenori KAWAMURA, M.D., Kyowa Medical Clinic,
(Our note: After reading through this research, you will be saying,
“why am I not doing this already?” —
The research is absolutely compelling)

In November ’95 I presented a hypothesis known by the title : ‘Water Regulating Theory (Hayashi’s Model)’ in a US health magazine (3). It says that active oxygen could be scavenged or reduced by atomic hydrogen, which results in production of H2O to give again a birthplace for every life form. My hypothesis was born from the clinical observation study in our clinic. Since May ’85 we have confirmed thousands of clinical improvements, obtained solely by exchanging drinking (as well as cooking water) from tap water to reduced water.
Those improvements were very exciting and some of them were considered to be miraculous at that time, when Shirahata’s paper was not yet submitted. It should be remembered that such putrefied metabolites are the same ones which are produced as a result of putrefaction of protein. The difference lies only in the fact that the former putrefaction process is brought about by intestinal microbes, whereas the latter is brought about by airborne microbes (Fig.2, 3). Based on these facts, I proposed a hypothesis ‘Pre-and posthepatic Organ Theory’ in 1988, 1989 & 1990 at the International Symposium on ‘Man and His Environment in Health and Disease’ held at Dallas, Texas, USA (Fig.4).
I stated that, as it is impossible to purify the polluted water in the St.Laurence River without purifying the polluted water in Lake Ontario, so it should be impossible to improve the disorders of post hepatic organs, without trying to improve the disorder of pre hepatic organs, namely putrefaction in gastrointestinal tract. Such clinical experiences have led us to recognize that reduced water is not only effective for restoration of intestinal flora metabolism, but also could be effective in scavenging active oxygen. Our clinical observation data, and my hypothesis, were delivered to Prof. Shirahata in April 1996 and his research has since started.
Shirahata’s paper means that cell metabolism, either microbial or cancerous, depends on its intracellular water, namely cell metabolism. This can vary according to the property of intracellular water, i.e. hydrogen-rich or not.. And even cancer cells might lose their characteristic feature of unlimited proliferation when they are immersed in hydrogen-rich water, originated and developed in Japan, but totally unknown in the past throughout the world. The solution might now be in our hands. Our ‘new water’ should be the first choice for all of us to take, as has been suggested by Happe, Shirahata and ourselves.
Case presentation on improvements of diabetes, hepatoma & atopic dermatitis.
CLINICAL IMPROVEMENTS OBTAINED FROM THE INTAKE OF REDUCED WATER
HAYASHI, Hidemitsu, M.D., Water Institute, & KAWAMURA, Munenori, M.D., Kyowa Medical Clinic, (1985-2000)
Experiences of pregnant women who took reduced water during their pregnancy; almost no emesis, smooth delivery, slight jaundice, enough lactation, smooth and satisfactory growth of newborns…..
Devices to produce reduced water were introduced into our clinic in May 1985. Based on the clinical experiences obtained in the past 15 years, it can be said that introduction of naturally reduced water (using H-01 Active Hydrogen Generator) or electrolyzed-reduced water for drinking and cooking purpose for in-patients should be the very prerequisite in our daily medical practices.
It is because any dietary recipe cannot be a scientific one if property of water taken by the patients is not taken into consideration.
The Ministry of Health and Welfare in Japan announced in 1965 that the intake of reduced water is effective for restoration of intestinal flora metabolism.
Sanetaka Shirahata, Shirgeru Kabayama, Mariko Nakano, Takumi Miura, Kenichi Kusumoto, Miho Gotoh, Hidemitsu Hayashi, Kazumichi Otsubo, Shinkatsu Morisawa, and Yoshinori Katakura
Published in: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, Vol. 234, No.1, May 8, 1997
Active oxygen species or free radicals are considered to cause extensive oxidative damage to biological macromolecules, which brings about a variety of diseases as well as aging. The ideal scavenger for active oxygen should be 'active hydrogen'. 'Active hydrogen' can be produced in reduced water near the cathode during electrolysis of water. Reduced water exhibits high pH, low dissolved oxygen (DO), extremely high dissolved molecular hydrogen (DH), and extremely negative redox potential (RP) values. Strongly electrolyzed-reduced water, as well as ascorbic acid, (+)-catechin and tannic acid, completely scavenged O.-2 produced by the hypoxanthine-xanthine oxidase (HX-XOD) system in sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0). The superoxide dismutase (SOD)-like activity of reduced water is stable at 4 degrees C for over a month and was not lost even after neutralization, repeated freezing and melting, deflation with sonication, vigorous mixing, boiling, repeated filtration, or closed autoclaving, but was lost by opened autoclaving or by closed autoclaving in the presence of tungsten trioxide which efficiently adsorbs active atomic hydrogen. Water bubbled with hydrogen gas exhibited low DO, extremely high DH and extremely low RP values, as does reduced water, but it has no SOD-like activity. These results suggest that the SOD-like activity of reduced water is not due to the dissolved molecular hydrogen but due to the dissolved atomic hydrogen (active hydrogen). Although SOD accumulated H2O2 when added to the HX-XOD system, reduced water decreased the amount of H2O2 produced by XOD. Reduced water, as well as catalase and ascorbic acid, could directly scavenge H2O2. Reduced water suppresses single-strand breakage of DNA b active oxygen species produced by the Cu(II)-catalyzed oxidation of ascorbic acid in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that reduced water can scavenge not only O2.- and H2O2, but also 1O2 and .OH.
Ikuroh Ohsawa, Masahiro Ishikawa, Kumiko Takahashi, Megumi Watanabe, Kiyomi Nishimaki, Kumi Yamagata, Ken-ichiro Katsura, Yasuo Katayama, Sadamitsu Asoh and Shigeo Ohta
Published in: Nature Medicine: Advance Online Publication, published on line May 7, 2007 Nature Publishing Group, http://www.nature.com/naturemedicine.
Abstract
Acute oxidative stress induced by ischemia-reperfusion or inflammation causes serious damage to tissues, and persistent oxidative stress is accepted as one of the causes of many common diseases including cancer. We show here that hydrogen (H2) has potential as an antioxidant in preventive and therapeutic applications. We induced acute oxidative stress in cultured cells by three independent methods. H2 selectively reduced the hydroxyl radical, the most cytotoxic of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and effectively protected cells; however, H2 did not react with other ROS, which possess physiological roles. We used an acute rat model in which oxidative stress damage was induced in the brain by focal ischemia and reperfusion. The inhalation of H2 gas markedly suppressed brain injury by buffering the effects of oxidative stress. Thus H2 can be used as an effective antioxidant therapy; owing to its ability to rapidly diffuse across membranes, it can reach and react with cytotoxic ROS and thus protect against oxidative damage.
Sizuo Kajiyama, Goji Hasegawa, Mai Asano, Hiroko Hosoda, michiaki Fukui, Naoto Nakamura, Jo Kitawaki, saeko Imai, Koji Nakano, Mitsuhiro Ohta, Tetsui Adachi, Hiroshi Obayashi, Toshikazu Yoshikawa Published in: Science Direct; Nutrition Research 28 (2008) 137-143; Elsevier Available online at www.sciencedirect.com : Nutrition Research www.elsevier.com/locate/nutres
Abstract
Oxidative stress is recognized widely as being associated with various disorders including diabetes, hypertension, and atherosclerosis. It is well established that hydrogen has a reducing action. We therefore investigated the effects of hydrogen-rich water intake on lipid and glucose metabolism in patients with either type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) or impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). We performed a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study in 30 patients with T2DM controlled by diet and exercise therapy and 6 patients with IGT. The patients consumed either 900 mL/d of hydrogen-rich pure water or 900 mL of placebo pure water for 8 weeks, with a 12-week washout period. Several biomarkers of oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and glucose metabolism, assessed by an oral glucose tolerance test, were evaluated at baseline and at 8 weeks. Intake of hydrogen-rich water was associated with significant decreases in the levels of modified low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (ie, modifications that increase the net negative charge of LDL), small dense LDL, and urinary 8-isoprostanes by 15.5% (P < .01), 5.7% (P < .05), and 6.6% (P < .05), respectively. Hydrogen-rich water intake was also associated with a trend of decreased serum concentrations of oxidized LDL and free fatty acids, and increased plasma levels of adiponectin and extracellular-superoxide dismutase. In 4 of 6 patients with IGT, intake of hydrogen-rich water normalized the oral glucose tolerance test. In conclusion, these results suggest that supplementation with hydrogen-rich water may have a beneficial role in prevention of T2DM and insulin resistance.
Kazufumi Nagata, Naomi Nakashima-Kamimura, Toshio Mikami, Ikuroh Ohsawa, Shigeo Ohta
Neuropsychopharmacology advance online publication 18 June 2008; doi:10.1038/npp.2008.95
Abstract
We have reported that hydrogen (H2) acts as an efficient antioxidant by gaseous rapid diffusion. When water saturated with hydrogen (hydrogen water) was placed into the stomach of a rat, hydrogen was detected at several M level in blood. Because hydrogen gas is unsuitable for continuous consumption, we investigated using mice whether drinking hydrogen water ad libitum, instead of inhaling hydrogen gas, prevents cognitive impairment by reducing oxidative stress. Chronic physical restraint stress to mice enhanced levels of oxidative stress markers, malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, in the brain, and impaired learning and memory, as judged by three different methods: passive avoidance learning, object recognition task, and the Morris water maze. Consumption of hydrogen water ad libitum throughout the whole period suppressed the increase in the oxidative stress markers and prevented cognitive impairment, as judged by all three methods, whereas hydrogen water did not improve cognitive ability when no stress was provided. Neural proliferation in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus was suppressed by restraint stress, as observed by 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine incorporation and Ki-67 immunostaining, proliferation markers. The consumption of hydrogen water ameliorated the reduced proliferation although the mechanistic link between the hydrogen-dependent changes in neurogenesis and cognitive impairments remains unclear. Thus, continuous consumption of hydrogen water reduces oxidative stress in the brain, and prevents the stress-induced decline in learning and memory caused by chronic physical restraint. Hydrogen water may be applicable for preventive use in cognitive or other neuronal disorders.
Kyota Fujita1, Toshihiro Seike1, Noriko Yutsudo2, Mizuki Ohno2, Hidetaka Yamada2, Hiroo Yamaguchi2, Kunihiko Sakumi2, Yukiko Yamakawa1, Mizuho A. Kido3, Atsushi Takaki4, Toshihiko Katafuchi4, Yoshinori Tanaka5, Yusaku Nakabeppu2#, Mami Noda
Laboratory of Pathophysiology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 2 Division of Neurofunctional Genomics, Medical Institute of Bioregulation, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 3 Department of Oral Anatomy and Cell Biology, Graduate School of Dental Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 4 Department of Integrative Physiology, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 5 R&D Center, Home Appliances Manufacturing Business Unit, Panasonic Electric Works Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan
PLoS ONE | www.plosone.org 1 September 2009 | Volume 4 | Issue 9 |
It has been shown that molecular hydrogen (H2) acts as a therapeutic antioxidant and suppresses brain injury by buffering the effects of oxidative stress. Chronic oxidative stress causes neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease (PD). Here, we show that drinking H2-containing water significantly reduced the loss of dopaminergic neurons in PD model mice using both acute and chronic administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). The concentration-dependency of H2 showed that H2 as low as 0.08 ppm had almost the same effect as saturated H2 water (1.5 ppm). MPTP-induced accumulation of cellular 8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG), a marker of DNA damage, and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), a marker of lipid peroxidation were significantly decreased in the nigro-striatal dopaminergic pathway in mice drinking H2-containing water, whereas production of superoxide (O2•−) detected by intravascular injection of dihydroethidium (DHE) was not reduced significantly. Our results indicated that low concentration of H2 in drinking water can reduce oxidative stress in the brain. Thus, drinking H2-containing water may be useful in daily life to prevent or minimize the risk of life style-related oxidative stress and neurodegeneration.
Ikuroh Ohsawaa, b, Kiyomi Nishimakia, Kumi Yamagataa, Masahiro Ishikawaa and Shigeo Ohtaa,
Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Institute of Development and Aging Sciences, Nippon Medical School, 1-396 Kosugi-cho, Nakahara-ku, Kawasaki, Kanagawa 211-8533, Japan
The Center of Molecular Hydrogen Medicine, Institute of Development and Aging Sciences, Nippon Medical School, Kawasaki 211-8533, Japan
Received 16 October 2008. Available online 6 November 2008.
Abstract
Oxidative stress is implicated in atherogenesis; however most clinical trials with dietary antioxidants failed to show marked success in preventing atherosclerotic diseases. We have found that hydrogen (dihydrogen; H2) acts as an effective antioxidant to reduce oxidative stress [I. Ohsawa, M. Ishikawa, K. Takahashi, M. Watanabe, K. Nishimaki, K. Yamagata, K. Katsura, Y. Katayama, S, Asoh, S. Ohta, Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals, Nat. Med. 13 (2007) 688–694]. Here, we investigated whether drinking H2-dissolved water at a saturated level (H2–water) ad libitum prevents arteriosclerosis using an apolipoprotein E knockout mouse (apoE−/−), a model of the spontaneous development of atherosclerosis. ApoE−/− mice drank H2–water ad libitum from 2 to 6 month old throughout the whole period. Atherosclerotic lesions were significantly reduced by ad libitum drinking of H2–water (p = 0.0069) as judged by Oil-Red-O staining series of sections of aorta. The oxidative stress level of aorta was decreased. Accumulation of macrophages in atherosclerotic lesions was confirmed. Thus, consumption of H2-dissolved water has the potential to prevent arteriosclerosis.
Naomi Nakashima-Kamimura1, Takashi Mori3, Ikuroh Ohsawa1, 2, Sadamitsu Asoh1 and Shigeo Ohta1
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, Volume 64, Number 4 / September, 2009, Friday, January 16, 2009
Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Institute of Development and Aging Sciences, Nippon Medical School, Kawasaki Kanagawa, 211-8533, Japan
The Center of Molecular Hydrogen Medicine, Institute of Development and Aging Sciences, Nippon Medical School, Kawasaki Kanagawa, 211-8533, Japan
Institute of Medical Science, Saitama Medical Center/University, Kawagoe Saitama, 350-8550, Japan
Received: 24 September 2008 Accepted: 30 December 2008 Published online: 16 January 2009
Abstract
Purpose Cisplatin is a widely used anti-cancer drug in the treatment of a wide range of tumors; however, its application is limited by nephrotoxicity, which is affected by oxidative stress. We have reported that molecular hydrogen (H2) acts as an efficient antioxidant (Ohsawa et al. in Nat Med 13:688–694, 2007). Here we show that hydrogen efficiently mitigates the side effects of cisplatin by reducing oxidative stress.
Methods Mice were administered cisplatin followed by inhaling hydrogen gas (1% H2 in air). Furthermore, instead of inhaling hydrogen gas, we examined whether drinking water containing hydrogen (hydrogen water; 0.8 mM H2 in water) is applicable by examining oxidative stress, mortality, and body-weight loss. Nephrotoxicity was assessed by morphological changes, serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels.
Results Inhalation of hydrogen gas improved mortality and body-weight loss caused by cisplatin, and alleviated nephrotoxicity. Hydrogen was detected in blood when hydrogen water was placed in the stomach of a rat. Consuming hydrogen water ad libitum also reduced oxidative stress, mortality, and body-weight loss induced by cisplatin in mice. Hydrogen water improved metamorphosis accompanying decreased apoptosis in the kidney, and nephrotoxicity as assessed by serum creatinine and BUN levels. Despite its protective effects against cisplatin-induced toxicity, hydrogen did not impair anti-tumor activity of cisplatin against cancer cell lines in vitro and tumor-bearing mice in vivo.
Conclusion Hydrogen has potential for improving the quality of life of patients during chemotherapy by efficiently mitigating the side effects of cisplatin.
Neurosci Lett. 2009 Apr 3;453(2):81-5. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Fu Y, Ito M, Fujita Y, Ito M, Ichihara M, Masuda A, Suzuki Y, Maesawa S, Kajita Y, Hirayama M, Ohsawa I, Ohta S, Ohno K.
Division of Neurogenetics, Center for Neurological Diseases and Cancer, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan.
Molecular hydrogen serves as an antioxidant that reduces hydroxyl radicals, but not the other reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. In the past year, molecular hydrogen has been reported to prevent or ameliorate eight diseases in rodents and one in human associated with oxidative stress. In Parkinson's disease, mitochondrial dysfunction and the associated oxidative stress are major causes of dopaminergic cell loss in the substantia nigra. We examined effects of approximately 50%-saturated molecular hydrogen in drinking water before or after the stereotactic surgery on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced nigrostrital degeneration in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Methamphetamine-induced behavioral analysis showed that molecular hydrogen prevented both the development and progression of the nigrostrital degeneration. Tyrosine hydroxylase staining of the substantia nigra and striatum also demonstrated that pre- and post-treatment with hydrogen prevented the dopaminergic cell loss. Our studies suggest that hydrogen water is likely able to retard the development and progression of Parkinson's disease.
Hideaki Oharazawa,1 Tsutomu Igarashi,2 Takashi Yokota,3 Hiroaki Fujii,4 Hisaharu Suzuki,5 Mitsuru Machide,6 Hiroshi Takahashi,7 Shigeo Ohta,8 and Ikuroh
Ohsawa9 1Department of Ophthalmology, Musashikosugi Hospital, Nippon Medical School, Kawasaki, Japan 2Department of Ophthalmology, Nippon Medical School, Tokyo, Japan 3Department of Molecular Biology, Institute of Development and Aging Sciences, Nippon Medical School, Kawasaki, Japan 4Department of Ophthalmology, Musashikosugi Hospital, Nippon Medical School, Kawasaki, Japan 5Department of Ophthalmology, Nippon Medical School, Tokyo, Japan 6The Center of Molecular Hydrogen Medicine, Institute of Development and Aging Sciences, Nippon Medical School, Kawasaki, Japan 7Department of Ophthalmology, Nippon Medical School, Tokyo, Japan 8Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Institute of Development and Aging Sciences, Nippon Medical School, Kawasaki, Japan 9The Center of Molecular Hydrogen Medicine, Institute of Development and Aging Sciences, Nippon Medical School, Kawasaki, Japan
Correspondence: Ikuroh Ohsawa, Email: [email protected]
Abstract
PURPOSE. Retinal ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury by transient elevation of intraocular pressure (IOP) is known to induce neuronal damage through the generation of reactive oxygen species. Previous studies indicate that molecular hydrogen (H2) is an efficient antioxidant gas that selectively reduces the hydroxyl radical ( OH) and suppresses oxidative stress-induced injury in several organs. This study was conducted to explore the neuroprotective effect of H2-loaded eye drops on retinal I/R injury.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997 May 8;234(1):269-74.
Shirahata S, Kabayama S, Nakano M, Miura T, Kusumoto K, Gotoh M, Hayashi H, Otsubo K, Morisawa S, Katakura Y.
Institute of Cellular Regulation Technology, Graduate School of Genetic Resources Technology, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan. [email protected]
Active oxygen species or free radicals are considered to cause extensive oxidative damage to biological macromolecules, which brings about a variety of diseases as well as aging. The ideal scavenger for active oxygen should be 'active hydrogen'. 'Active hydrogen' can be produced in reduced water near the cathode during electrolysis of water. Reduced water exhibits high pH, low dissolved oxygen (DO), extremely high dissolved molecular hydrogen (DH), and extremely negative redox potential (RP) values. Strongly electrolyzed-reduced water, as well as ascorbic acid, (+)-catechin and tannic acid, completely scavenged O.-2 produced by the hypoxanthine-xanthine oxidase (HX-XOD) system in sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0). The superoxide dismutase (SOD)-like activity of reduced water is stable at 4 degrees C for over a month and was not lost even after neutralization, repeated freezing and melting, deflation with sonication, vigorous mixing, boiling, repeated filtration, or closed autoclaving, but was lost by opened autoclaving or by closed autoclaving in the presence of tungsten trioxide which efficiently adsorbs active atomic hydrogen. Water bubbled with hydrogen gas exhibited low DO, extremely high DH and extremely low RP values, as does reduced water, but it has no SOD-like activity. These results suggest that the SOD-like activity of reduced water is not due to the dissolved molecular hydrogen but due to the dissolved atomic hydrogen (active hydrogen). Although SOD accumulated H2O2 when added to the HX-XOD system, reduced water decreased the amount of H2O2 produced by XOD. Reduced water, as well as catalase and ascorbic acid, could directly scavenge H2O2. Reduced water suppresses single-strand breakage of DNA b active oxygen species produced by the Cu(II)-catalyzed oxidation of ascorbic acid in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that reduced water can scavenge not only O2.- and H2O2, but also 1O2 and .OH.
PMID: 9169001 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
Additional comment on above article by Dr. Shirahata:
Dr.Sanetaka Shirahata
Graduate school of Genetic Resources Technology, Kyushu University, 6-10-1 Hakozaki, Higashi-ku, Fukuoka 812-8581, Japan.
It has long been established that reactive oxygen species (ROS) cause many types of damage to biomolecules and cellular structures, that, in turn result in the development of a variety of pathologic states such as diabetes, cancer and aging. Reduced water is defined as anti-oxidative water produced by reduction of water. Electrolyzed reduced water (ERW) has been demonstrated to be hydrogen-rich water and can scavenge ROS in vitro (Shirahata et al., 1997). The reduction of proton in water to active hydrogen (atomic hydrogen, hydrogen radical) that can scavenge ROS is very easily caused by a weak current, compared to oxidation of hydroxyl ion to oxygen molecule. Activation of water by magnetic field, collision, minerals etc. will also produce reduced water containing active hydrogen and/or hydrogen molecule. Several natural waters such as Hita Tenryosui water drawn from deep underground in Hita city in Japan, Nordenau water in Germany and Tlacote water in Mexico are known to alleviate various diseases. We have developed a sensitive method by which we can detect active hydrogen existing in reduced water, and have demonstrated that not only ERW but also natural reduced waters described above contain active hydrogen and scavenge ROS in cultured cells. ROS is known to cause reduction of glucose uptake by inhibiting the insulin-signaling pathway in cultured cells. Reduced water scavenged intracellular ROS and stimulated glucose uptake in the presence or absence of insulin in both rat L6 skeletal muscle cells and mouse 3T3/L1 adipocytes. This insulin-like activity of reduced water was inhibited by wortmannin that is specific inhibitor of PI-3 kinase, a key molecule in insulin signaling pathways. Reduced water protected insulin-responsive cells from sugar toxicity and improved the damaged sugar tolerance of type 2 diabetes model mice, suggesting that reduced water may improve insulin-independent diabetes mellitus. Cancer cells are generally exposed to high oxidative stress. Reduced water cause impaired tumor phenotypes of human cancer cells, such as reduced growth rate, morphological changes, reduced colony formation ability in soft agar, passage number-dependent telomere shortening, reduced binding abilities of telomere binding proteins and suppressed metastasis. Reduced water suppressed the growth of cancer cells transplanted into mice, demonstrating their anti-cancer effects in vivo. Reduced water will be applicable to not only medicine but also food industries, agriculture, and manufacturing industries.
Copyright 2002 - 2024. All rights reserved.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. No product mentioned herein is intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. If you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition, consult your physician before making any lifestyle change, including trying a new product or food.
The information on this website is intended as a sharing of knowledge and information from the research and experience of the Healthy-Living.Org staff and contributors. It is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and it is not intended as medical advice. You should not use the information on this site for diagnosis or treatment of any health problem or for modification of any medication regimen. You should consult with a healthcare professional before starting any diet, exercise or supplementation program, before starting or discontinuing any medication, or if you suspect you have a health problem. You should keep in mind that cited references to ongoing nutritional scientific study are most likely not accepted by the FDA as conclusive. These references and mentions of benefits experienced by others are disavowed as product claims and are only included for educational value and as starting points for your own research. No food or supplement can be considered safe for all individuals. What may benefit 999,999 of a million people may harm you. Therefore, no one can take responsibility for your health except you in concert with your trusted health professional.